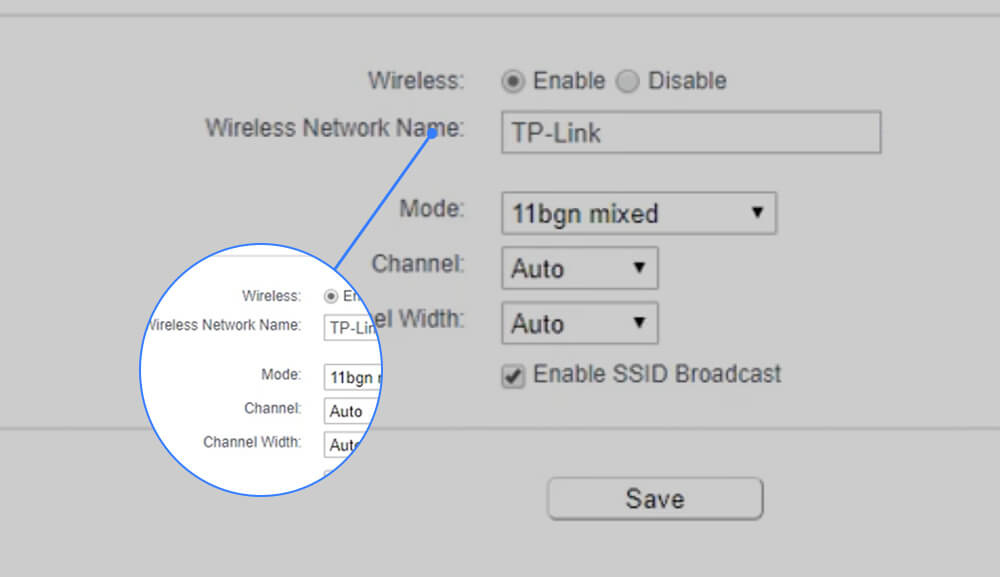
SSID or Service Set Identifier is an acronym that is related to Wi-Fi Networks. SSID is basically the name of the Wi-Fi Network that is either set by default by the manufacturer or a customized name set by the owner. SSIDs are meant for the identification of Wi-Fi networks, without them you wouldn’t be able to distinguish between different networks.
SSIDs are meant to be unique so, you can connect to the correct network. When you buy a new router from a manufacturer then the network usually has a default SSID, indicating the name of the manufacturer, but it is good that you change the SSID of your network to a custom name of your choice, so people can connect to your network without any difficulty.
An SSID can be up to 32 characters in length with no lower limit, and it may include special characters, spaces, periods, underscores, and dashes. SSIDs are case-sensitive and there is a huge difference between an SSID in lower-case and an SSID in upper-case.
All the routers and Wi-Fi devices broadcast their SSIDs and nearby devices can connect to those networks using SSIDs. If the network is open then anyone can join the network just with the correct SSID and if it is password protected then you would need to enter the passphrase in order to connect to the network.
If there are multiple networks with the same SSID, for instance, there are two networks with the SSID “Home” then there can arise complications. Some devices will connect to the network with the strongest signal while some devices will prefer to join the network that they discover first.
If there are other networks with the same SSID then your device may face complications while connecting, therefore, it is good that you change the SSID if there are other networks with the same SSID available nearby.